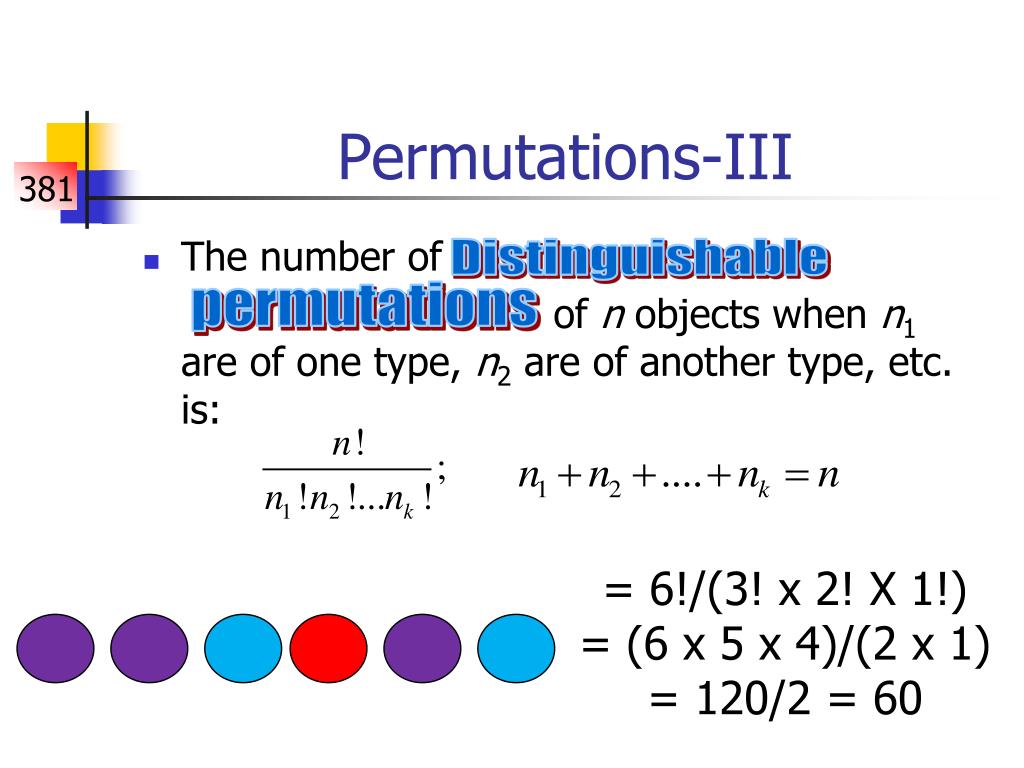
Probability Arrangements And Combinations . this section covers permutations and combinations. calculate probabilities with permutations. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. The number of ways of arranging n unlike. In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a) (c, a) are 2 different arrangements. this article presents the differences between arrangements, permutations, and combinations in. Probability & statistics 1 syllabus, written by the maths experts at save. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations.
from www.slideserve.com
The number of ways of arranging n unlike. this article presents the differences between arrangements, permutations, and combinations in. For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a) (c, a) are 2 different arrangements. Probability & statistics 1 syllabus, written by the maths experts at save. when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. this section covers permutations and combinations. In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths:
PPT ProbabilityIII (Permutations and Combinations) PowerPoint
Probability Arrangements And Combinations when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. calculate probabilities with permutations. For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a) (c, a) are 2 different arrangements. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: this article presents the differences between arrangements, permutations, and combinations in. In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. this section covers permutations and combinations. The number of ways of arranging n unlike. Probability & statistics 1 syllabus, written by the maths experts at save. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations.
From ciemathsolutions.blogspot.com
Cambridge AS Level Mathematics 9709 (Probability & Statistics 1 Probability Arrangements And Combinations The number of ways of arranging n unlike. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.youtube.com
Probability and Counting Rules Combination Examples YouTube Probability Arrangements And Combinations revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. The number of ways of arranging n unlike. calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Probability and statistics PowerPoint Presentation, free download Probability Arrangements And Combinations In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. this article presents the differences between arrangements, permutations, and combinations in. The number of ways of arranging n unlike. when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. this section covers permutations and. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.youtube.com
Probability with Counting Principles Permutation Combination Concepts Probability Arrangements And Combinations In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. this section covers permutations and combinations. Probability &. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.ck12.org
Combinations Example 2 ( Video ) Probability CK12 Foundation Probability Arrangements And Combinations calculate probabilities with permutations. when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. this section covers permutations and combinations. The number of ways of arranging n unlike. the arrangements of a set. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.studypug.com
Understanding permutations vs. combinations StudyPug Probability Arrangements And Combinations revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: this section covers permutations and combinations. calculate probabilities with permutations. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. The number of ways of arranging n unlike. For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a). Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.slideshare.net
Probability Day 3 Permutations and Combinations Probability Arrangements And Combinations the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. The number of ways of arranging n unlike. Probability & statistics 1 syllabus, written by the maths experts at save. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Binomial Probability Distribution PowerPoint Presentation, free Probability Arrangements And Combinations For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a) (c, a) are 2 different arrangements. calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; this article presents the differences between arrangements, permutations, and combinations in. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities,. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From kidsworksheetfun.com
Probability Permutations And Combinations Worksheet With Answers Pdf Probability Arrangements And Combinations In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. this section covers permutations and combinations. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: The number of ways of arranging n unlike. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. For example, (a,. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.youtube.com
Finding Probabilities Using Combinations YouTube Probability Arrangements And Combinations For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a) (c, a) are 2 different arrangements. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths:. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.scribd.com
S1 Arrangements and Combinations PDF PDF Standard Deviation Probability Arrangements And Combinations revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: this article presents the differences between arrangements, permutations, and combinations in. calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. calculate probabilities with permutations. Probability & statistics 1 syllabus, written by the maths experts at. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From igcseatmathematicsrealm.blogspot.com
Probability Tree Diagram IGCSE at Mathematics Realm Probability Arrangements And Combinations this article presents the differences between arrangements, permutations, and combinations in. calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. this section covers permutations and combinations. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. For example, (a, c) (a, c). Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From materialcampusreflexed.z5.web.core.windows.net
Probability Permutations And Combinations Worksheet With Ans Probability Arrangements And Combinations calculate probabilities with permutations. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order of the elements that form them. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. The number of ways of arranging n unlike. calculate. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.cuemath.com
Combinations Definition, Formula, Examples, FAQs Probability Arrangements And Combinations when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. this section covers permutations and combinations. For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a) (c, a) are 2 different arrangements. Probability & statistics 1 syllabus, written by the maths experts at save. In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. In this post,. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From www.mashupmath.com
Probability Tree Diagrams Explained! — Mashup Math Probability Arrangements And Combinations In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. calculate probabilities with permutations. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: this section covers permutations and combinations. the arrangements of a set are characterized by the order. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From education-portal.com
How to Calculate the Probability of Combinations Video & Lesson Probability Arrangements And Combinations calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; this section covers permutations and combinations. For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a) (c, a) are 2 different arrangements. revision notes on 2.2.1 arrangements & factorials for the cie a level maths: when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. In. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From study.com
Finding Probabilities Using Combinations in One Step Algebra Probability Arrangements And Combinations In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. In our earlier discussion of theoretical probabilities, the first. calculate probabilities with permutations. Probability & statistics 1 syllabus, written by the maths experts at save. For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a) (c, a) are 2 different arrangements. when calculating probabilities, you often need to. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.
From donsteward.blogspot.com
MEDIAN Don Steward mathematics teaching probability arrangements Probability Arrangements And Combinations In this post, i’ll show you how to calculate the number. For example, (a, c) (a, c) and (c, a) (c, a) are 2 different arrangements. calculate the probability of two independent events occurring; calculate probabilities with permutations. when calculating probabilities, you often need to calculate the number of possible combinations. In our earlier discussion of theoretical. Probability Arrangements And Combinations.